Knee
Conservative Management:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Resting the knee and avoiding activities that exacerbate pain or discomfort can help promote healing.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs to the knee can help reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation.
- Compression and Elevation: Using compression bandages and elevating the knee can also help reduce swelling and promote circulation.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may be recommended to manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises, stretches, and manual therapy techniques can help strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and restore range of motion.
- Bracing or Orthotics: Knee braces or orthotic devices, such as shoe inserts, may be used to provide support, stability, and alignment to the knee joint.
Minimally Invasive Procedures:
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injection of corticosteroids into the knee joint can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain associated with conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or bursitis.
- Hyaluronic Acid Injections: Injection of hyaluronic acid (a lubricating fluid naturally found in the joint) can help improve joint function and reduce pain in people with knee osteoarthritis.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy involves injecting a concentrated solution of platelets from the patient’s own blood into the knee joint to promote tissue healing and reduce inflammation.
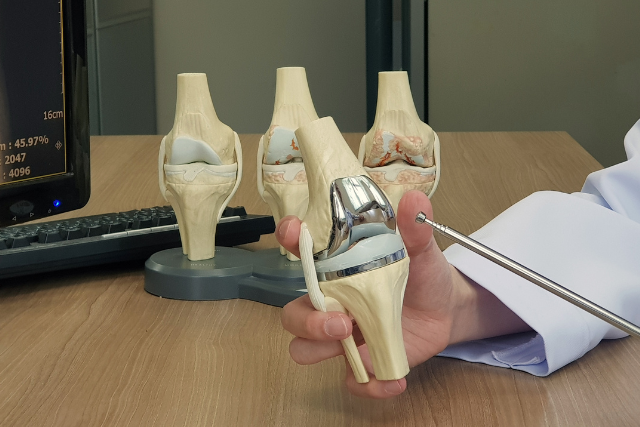

Surgical Intervention:
- Arthroscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive arthroscopic surgery may be performed to diagnose and treat various knee conditions, such as meniscus tears, ligament injuries (e.g., ACL tear), or cartilage damage.
- Partial Knee Replacement: In cases of isolated knee arthritis affecting only one compartment of the knee, a partial knee replacement may be considered, where only the damaged portion of the knee joint is replaced with a prosthetic implant.
- Total Knee Replacement (TKR): For severe knee arthritis or irreparable joint damage, total knee replacement surgery may be recommended. This involves replacing the entire knee joint with prosthetic components made of metal and plastic.
Rehabilitation and Recovery:
- Following any knee treatment, rehabilitation plays a crucial role in restoring function, mobility, and strength to the knee joint.
- Physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises are typically prescribed to help improve muscle strength, joint stability, and range of motion.
- Patients are advised to follow postoperative protocols and guidelines provided by their healthcare provider to ensure optimal recovery and long-term success.

